B2B SaaS sales require a structured, repeatable process to drive consistent growth and customer acquisition. Without one, even the most innovative product can struggle to scale.
The SaaS sales process is no less unique, with lots of room for growth and flexibility. To succeed in an SaaS business, it’s important to understand the sales process and best practices. It’s also crucial to choose the right selling model. If you run an SaaS startup, it’s important to understand how to hire good salespeople.
→ Need help building a high-performing SaaS sales team? Contact Peak to find top-tier sales talent.
What is the SaaS Sales Process?
The SaaS sales process is the series of key steps and strategies that a company follows to identify, target, attract, and convert potential customers into paying subscribers. The exact steps and stages may vary from one company to another.
The SaaS sales process is complex compared to traditional selling methods involving a one-time purchase of a product or software. For this reason, the SaaS sales process is typically longer and requires a more customer service focused approach to selling. When starting your SaaS sales journey, keep in mind that the initial investment in sales may appear costly. However, because SaaS is usually sold based on monthly or annual recurring revenue, the customers you acquire through this investment tend to have a higher lifetime value.
How long is the SaaS Sales Cycle?
The whole SaaS sales cycle can range from a few weeks long to several months long, with the average sales cycle around 80-90 days long based on common SaaS sales metrics. The SaaS sales process can vary from one company to another. It depends on deal size, the number of stakeholders, and the chosen model.
Sales cycles will be shorter for:
- Lower-priced products (under $5,000)
- Smaller companies with fewer stakeholders involved in the purchase decision
Sales cycles will be longer for:
- Higher priced products
- Larger companies with more stakeholders involved in the purchase decision
- Enterprise clients and SaaS sales models
Despite these variables, general principles in the SaaS sales cycle fit most companies. We’ve gathered the nine steps most commonly integrated into every company’s SaaS sales process.
The 9 Step SaaS Sales Process
Since the SaaS sales cycle length is overall longer in nature, it has more touch points between the potential customer and sales representative before a deal is made. This longer and more complex process requires sales representatives to be deeply educated in your software, highly motivated, and extremely agile in their skill set.
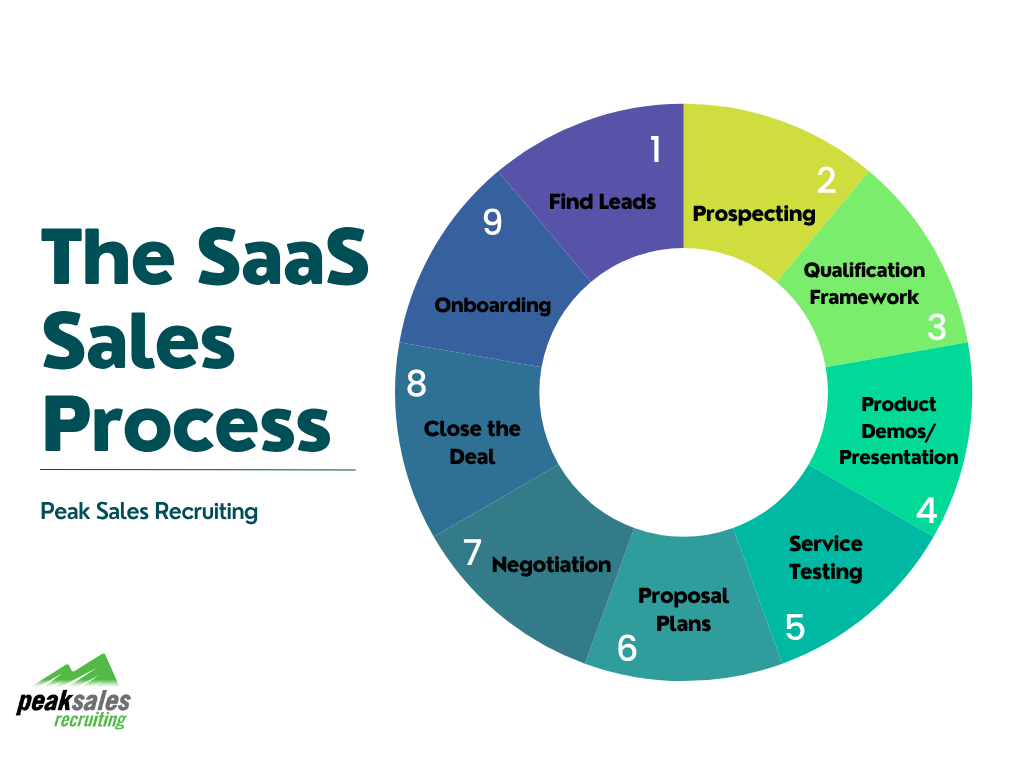
Step 1: Find Leads
While lead generation is a function of your marketing team, it’s worth mentioning how it can play a very crucial part in a SaaS selling process. Marketing helps people become familiar with your brand, enter your sales funnel, and understand how you can assist them by increasing brand awareness and encouraging engagement. It can even motivate users to sign up for free trials of a SaaS. You should aim to get in front of your customers before they’ve done extensive research on your product and your competitors. The earlier you gain control of the conversation and begin educating potential SaaS customers on your terms, the better.
Step 2: Focus on Prospecting
The B2B SaaS sales cycle really kicks into gear with prospecting, often led by your Sales Development Representatives, depending on the structure of your SaaS sales team. In this stage, warm leads may be contacted through a call or email. Cold calling and cold email can also be a part of prospecting.
Step 3: Set a Qualification Framework
This step is particularly important early on in SaaS sales. Sales reps spend a lot of time learning about potential customers. So, it’s crucial not to waste time on companies that aren’t a good fit. Through qualification, sales representatives determine if a prospect has needs that match with their service. Having a set qualification framework ensures consistent customer qualification.
This is also the time in the sales cycle when reps should check if the potential client has the budget for their service. They should also find out if they are speaking with the person who can make the final purchase decision.
Step 4: Provide Valuable Product Demos and Presentations
A cookie-cutter pitch doesn’t work in B2B SaaS sales. The best results are found when sales representatives are able to demonstrate the product features and benefits in a way that is tailored to the prospect. In today’s fast-paced SaaS landscape, customers also expect this to be done quickly. They won’t want to wait weeks or even days to get a demo from your team. You can show your product to B2B customers with a proof of concept (POC). This allows them to test the software with their existing systems before investing. In the product demonstration stage, representatives should be ready and able to answer questions and troubleshoot their software for potential customers as well.
Step 5: Offer Service Testing
In order for companies to experience a proof of concept, a testing or free trial period is often allowed. This hands-on time lets potential customers explore the software. They can see how it works, its full capabilities, and the value it brings to their company. Trials should be designed strategically to support customers in getting to know the value of the software while also guiding them into a sale in a timely manner. Read more about how to determine your trial length here.
Step 6: Have Clear Pricing & Proposal Plans
In the proposal stage, the SaaS sales representative gives the potential customer an overview of the available services, their recommendations for service, and lays out customized pricing or subscription plan costs.
Step 7: Prepare for Negotiation
Leading up to and during the negotiation stage, you want to ensure that you’ve educated and equipped your ‘champions’ inside the company. Key decision-makers will join at this stage. You and your company contacts should be ready to keep things moving. In negotiations, the sales rep will handle any remaining concerns, talk about terms, and agree on pricing.
Step 8: Close the Deal
Once both parties have committed to all terms, the deal is finalized, and the customer is guided into the onboarding process. This is where the company’s focus becomes customer success, and later, potential expansion or renewal is also important.
Step 9: Create a Positive Onboarding Experience
In SaaS Sales the purchase doesn’t end when the salesperson closes a deal. Once a prospect has become a customer, they’re likely to be paying for your SaaS on an ongoing basis and, therefore, need a continually positive sales experience to continue their subscription with you. Sales reps have the best chance to train, educate, and prepare customers during onboarding. You’ll reduce churn and increase your recurring revenue and customer lifetime value by nurturing new customers from the start. You’ll also set up your customer relationships for easier maintenance, smooth account management, and prime upselling opportunities in the future.
Which SaaS Sales Model is Right for Your Company or Startup?
Every fast growing SaaS company must select a model for their business and modify it to fit their service, sales process, and customer requirements. It’s normal for companies to blend SaaS models and structures to find a fit that is right for them.
In this article, we’re going to cover the most common models: subscription-based, freemium, pay-per-use, and enterprise.
The first of these three models can be structured for self-service, where the sales process relies more heavily on lead generation than on saas sales reps to close deals. They can also be more transactional. In this case, sales reps help guide the customer experience. They inspire prospects to convert, especially when they hesitate to pay a higher price for a SaaS product. The enterprise model always requires a solid SaaS sales team structure.
The Subscription Based Model – Ideal for predictable growth
This is the most common model for an SaaS company. If you choose this model for your company, you’ll have a more predictable recurring revenue and the costs incurred for automatic updates and regular software maintenance can be expected as well. This model allows you to remain flexible and can be scaled up or down to meet customer needs.
The Freemium Model – Best for driving high-volume user acquisition
The freemium model (a play on the words free and premium) offers a basic version of the software for free. Customers can easily say ‘yes’ to the free version, so a large number of users will sign up to try out your software. This low barrier to entry gives you an advantage down the line. Leads become even warmer prospects once they’re using your software. That means every upsell within your software is being offered to someone who is already actively engaging with your software.
This is an advantage you must leverage strategically, though.
If your free version features are too limited, users won’t find your SaaS beneficial and won’t buy your premium version. On the other hand, users who have everything they need on your free version won’t experience any pressure to upgrade. Some customers may stay with your free version forever. Still, many will opt for premium features if you balance your free and paid offerings well.
Consider what a customer needs to get a hands-on experience with your most impressive features while also limiting their access so that upgrading becomes the most convenient and economical option. You can limit how many entries or records a customer can make in the free version. You might also restrict the number of team members. High-end integrations can be reserved for premium users.
Scaling with this model can be a bit tricky, but isn’t impossible. You’ll need to consider how you’ll cover the cost of the SaaS sales and customer service staff needed to support a growing number of free members while you work to increase your paid memberships.
The Pay-Per-Use Model – Ideal for flexible or usage based offerings
In the pay-per-use model, customers do not pay a flat-rate recurring fee for your SaaS software. Instead, they’re charged in a tiered structure or based on thresholds based on what they use within your SaaS platform. Transactions, storage space, data transfer, or another relevant metric could measure usage. Users benefit from this model because they only pay for what they use, so their cost is directly proportional to the benefit they receive.
Companies benefit from this model because it’s easier to scale as usage fluctuates. When changes are too rapid, though, challenges can arise in managing or forecasting costs, leading to unpredictable expenses.
The Enterprise Model – Designed for large, high-value, B2B deals
If your SaaS solution has a high level of complexity and serves a very specific type of B2B client, you’ll want to consider an enterprise sales model. In this model, the sales cycle is heavily focused on outbound sales rather than on inbound marketing and sales.
This model works well for SaaS aimed at large companies, government agencies, and institutions with complex needs and big budgets. Given these unique characteristics of the model, the customers must make a significant financial investment as well as a significant time investment in purchasing the new SaaS. Customers might need to wait until their contracts end. They may also need to move their data and adjust their infrastructure to make the switch. While this increases the time it takes to convert and onboard a customer — and therefore increases the cost of the sale — it also means that customers have to go all in on the transition and are less likely to churn.
Finding the right balance between cost and features is crucial for lasting SaaS success. If the product is too complex for the price, your company will struggle to support its users appropriately. If you’re concerned about this, consider how to trim down your software to appeal to a broader audience or increase the price so that you can sell to bigger clients and adequately cover the cost of more intensive support.
4 SaaS Best Practices
No matter the model you choose for your SaaS business, you’ll want to follow a few best practices in your sales cycle. These practices ensure that every sales representative you hire is thoroughly trained in how to optimize their sales efforts.
1. Know Your Target Market
Sales reps who know their market well can qualify prospects easily. They can connect with buyers about specific needs and tackle industry challenges with a tailored pitch. Look for chances to network in your industry. Join online forums or groups where customers discuss their problems. They often ask questions that your software can solve.
2. Become a Team of Trusted Advisors
All SaaS solutions boil down to three types of solutions: increasing efficiency, creating cost savings, or saving time. As you get to know your target market, you’ll be able to clearly connect your customer’s problem with your solution. This level of expertise allows you to build reliability, trust, and rapport with customers that lays a foundation for beneficial long-term customer retention. Peak sales recommends these SaaS sales training programs to build an effective SaaS sales strategy.
3. Gain an In-Depth Experience of Your SaaS
Whenever possible, use your own SaaS software to gain and maintain a sense of what it is like to use your product first-hand. If you can’t do this regularly, think about involving your sales team. They can simulate use or shadow customers instead.. Experiential expertise beats observational expertise every time. Experiential expertise helps your reps gain personal insights. They learn the features and benefits of your product that matter most to each customer’s pain points.
4. Leverage Your Sales CRM
A customer relationship management (CRM) software isn’t just a place to house customer information. It can also become a place where you optimize your responsiveness and the quality of your customer service. Keep detailed notes as your team manages leads and tracks interactions throughout the sales pipeline. Even sales interactions and cycles that end in a ‘no’ the first, second, or third time could turn into a yes down the road. As you navigate those rejections and nurture those relationships, having an organized system for your client information will be invaluable.
Every Hire in SaaS Sales is High Stakes!
Since the sales cycle is longer and more complex than in other business models, it can also be far more expensive. Choosing eager, adaptable, and motivated professionals who understand your business model is paramount to your success.
Not just any great salesperson can sell SaaS, and we’d love to help make sure your team has the perfect mix of sales skills for your SaaS sales model. Contact us today to explore our network of qualified SaaS sales experts!




