Outbound prospecting is still one of the most effective ways to build a sales pipeline, especially in competitive B2B markets. While inbound leads can be valuable, they are not always predictable, consistent, or scalable on their own.
For sales teams that need more control over who they speak to and when, outbound prospecting remains a core part of the sales process.
Outbound is a skill set, and not every rep has it. Peak Sales Recruiting helps B2B companies hire sales reps who can identify target accounts and turn cold conversations into real opportunities. Contact us to learn more.
What Is Outbound Prospecting?
Outbound prospecting is the process of reaching out to potential customers who have not expressed interest in your product or service.
Instead of waiting for leads to come in, sales reps identify target accounts and initiate contact. They may use various communication channels such as:
- Cold email
- Cold calling
- Social media outreach
- Networking events
The primary goal of outbound prospecting is to start a relevant conversation with the right people (decision makers) and move qualified leads into your sales funnel. Outbound prospecting, when done right, creates steady opportunities. It also helps sales teams take control of their pipeline.
Inbound vs Outbound Prospecting
Inbound prospecting focuses on attracting prospects through marketing efforts. These prospects might download a resource, fill out a form, attend a webinar, or request a demo. Inbound tends to work best when marketing teams and sales align on targeting and follow-up, so interested prospects don’t slip through the cracks.
Outbound prospecting focuses on sales-led outreach. Sales reps identify good-fit accounts and initiate contact. Outbound prospecting can include cold outreach, but it also includes following up with prospects who already recognize your brand through marketing touchpoints, events, referrals, or past conversations.
Outbound prospecting is where reps:
- Identify a good-fit company within their ICP.
- Find the right decision makers.
- Send outreach messages (or make a call) that earn a response from the prospect.
- Move the conversation toward a first meeting.
Both approaches have a place in a healthy sales strategy. Inbound is often more efficient per-lead, but lead volume and quality can fluctuate. Outbound requires more effort upfront, but it allows teams to target specific industries and buyer personas that align with revenue goals.

How to Build an Outbound Prospecting Strategy
1. Define Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Success in outbound prospecting starts with a clearly defined Ideal Customer Profile (ICP).
Your ICP should outline the buyers and organizations that will gain the most from your offering. These are most likely to become long-term customers. The ICP typically includes firmographic data like industry, company size, revenue, and geography, as well as role-specific details like job titles and responsibilities.
Without a defined ICP, outbound efforts can quickly turn into high-volume activity with low-quality results.
Need a simple way to define your ICP without complicating it? Check out our full guide on building a strong sales ICP.
2. Build a Targeted Prospect List
Once your ICP is clearly defined, the next step is to build a prospect list that reflects it.
To be successful, prioritize quality over quantity. A smaller, well-researched list of accounts that closely match your ICP will almost always outperform a massive list built on loose criteria.
Prospect lists should be regularly cleaned, updated, and segmented based on buyer intent. This allows messaging to stay relevant as markets continue to change.
3. Create Clear, Relevant Messaging
Most prospects ignore outreach that seems generic or copied. The same rules apply to outbound messages. They work best when written for one specific person and their pain points, not an entire database of people.
Effective messaging always focuses on the prospect’s world first. Consider their role, their challenges, and what typically causes problems for people who are in similar situations. The goal is not to pitch immediately, but to earn a response by being relevant and concise.
Strong outbound messaging skips buzzwords. It keeps emails short and explains why the outreach matters to the prospect.
4. Choose the Right Channels
Outbound prospecting is rarely effective when it relies on a single channel. Most sales teams use a combination of cold email, cold calling, LinkedIn outreach, and occasional in-person networking events. Different prospects respond to different channels, and a multichannel contact strategy increases overall reach.
That said, channel choice should still reflect buyer behaviors. Senior decision-makers may prefer a short email or phone call, while others may engage more on LinkedIn or other platforms.
5. Start Prospecting and Stay Consistent
Consistency is key in outbound prospecting, including daily activity, structured follow-ups, and realistic expectations for response timing. Very few prospects reply on the first touch, which is why outbound prospecting cadences matter just as much as the initial message. 80% of sales deals require five follow-up calls. By not following up, money is being left on the table.
Sales teams that treat outbound prospecting as a repeatable, scalable process rather than a one-off effort tend to see stronger, and more predictable results.
How to Measure Outbound Prospecting Success
Success in outbound prospecting should be measured beyond just meetings booked. Some of the most important sales metrics include:
- Contact rate – measures how many successful connections you make with prospects.
- Response rate – measures how often prospects respond to your outreach.
- Qualification rate – assesses lead quality by tracking how many responses turn into real opportunities.
Tracking these metrics together provides a more complete picture of whether your outbound prospecting efforts are working or simply making noise.
Outbound Prospecting Tools
There are plenty of outbound prospecting tools on the market. These tools can boost your sales team’s productivity by reducing administrative tasks. However, they aren’t a substitute for smart targeting and careful execution.
The best tools support outbound prospecting in a few core areas:
1. Contact Data Tools
Contact data tools will help your sales team build lists, find the right decision-makers, and ensure they receive accurate contact details. This way, their outreach efforts won’t go to waste.
- ZoomInfo: One of the largest and most well-known platforms for B2B company and contact data. ZoomInfo is useful for list building and account research.
- Apollo.io: Apollo is a strong option for companies that are looking for contact data and basic outbound sequencing in a unified platform.
- Lusha: Helpful for quickly pulling phone numbers and email addresses. Lusha is more commonly used by smaller sales teams or individual sales representatives.
2. Sales Engagement and Sequencing Tools
Sequencing tools help sales teams maintain consistent follow-ups. They support prospecting cadences and help run consistent prospecting campaigns. They also allow for structured, multi-touch outreach.
- Outreach: Outreach is a popular tool used across B2B sales teams to build sequences, track prospect engagement, and manage outbound sales activity.
- Klenty: Sales engagement platform for running multi-touch outbound cadences. Offers strong customer relationship management (CRM) integration options as well.
- Reply.io: Often used by teams that rely heavily on cold outreach. Features multichannel outreach, email writing, and performance reporting.
3. Personalization Tools
Outbound is noisy. Your prospects can tell when they are getting a generic message also sent to 300 other prospects. Personalization tools help sales reps add a human touch to their outreach.
- Sendspark: Allows reps to create short, personalized videos at scale.
- Loom: Another video messaging option for prospecting, follow-ups, or sharing quick demos without booking a meeting.
- Lavender.ai: Helps reps improve email quality, clarity, and structure. This tool is especially useful for greener sales reps.
Final Thoughts on Outbound Prospecting
Outbound prospecting can often feel frustrating for sales reps because the effort must come before the results. When the strategy is clear, outbound prospecting is a reliable way to keep pipelines moving. This is especially true when inbound leads are inconsistent.
Winning outbound sales teams focus on four key areas:
- Strong targeting
- Clean contact data and lists
- Relevant messaging
- Consistent follow-up
Build a repeatable outbound prospecting system and stick with it; the results will follow.
Resources
For more sales resources, check out some of our recent blogs:
Emotional Intelligence in Sales: The Skill Top Performers Use to Close More Deals
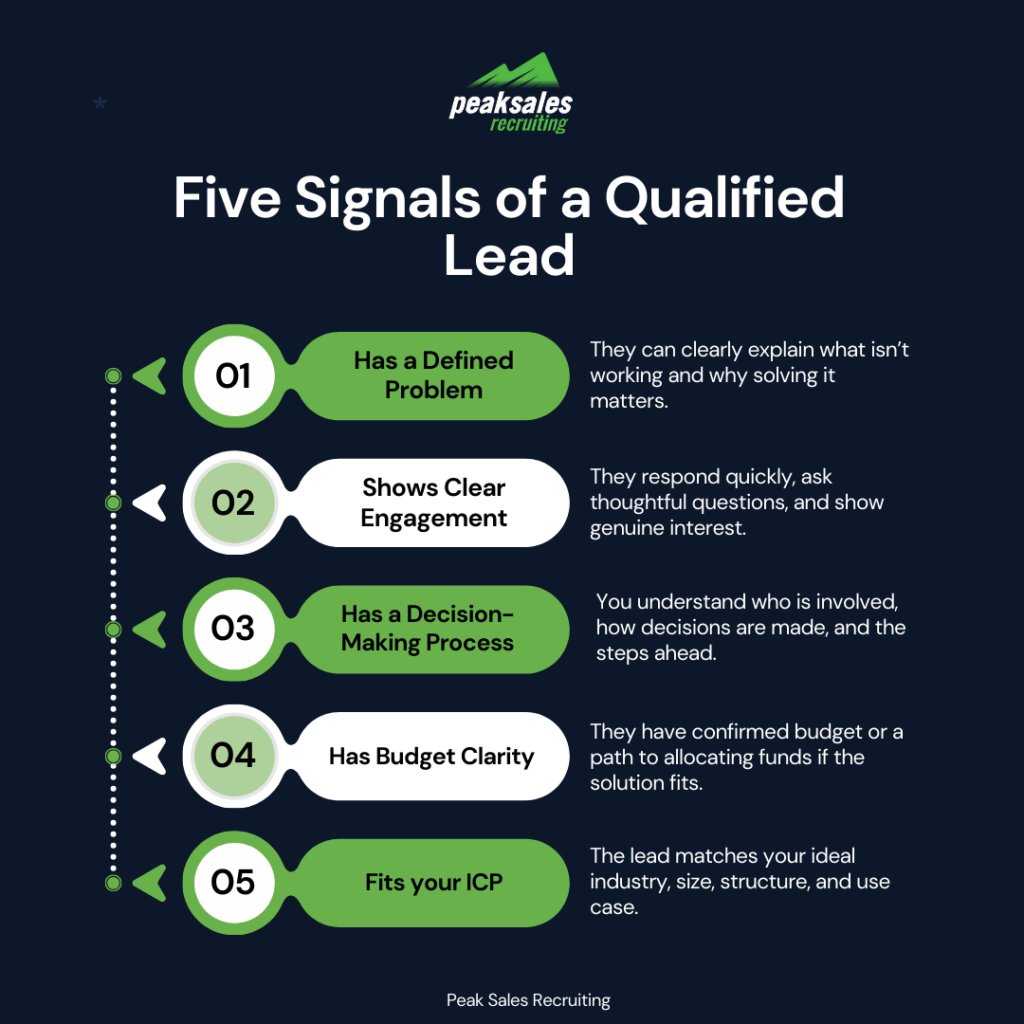
Lead Qualification Criteria Explained: What Buying Signals Matter Most
AI in Sales: The 2026 Guide to a Smarter, Faster, and More Predictive Sales Landscape